Definition of color weakness
The perception of colors is based on the ability to distinguish between the three primary colors red, green and blue. Humans mix all other colors together from these primary colors. Special light-sensitive cells are responsible for color vision: the cones, which are located in the retina. If the perception of one of these primary colors is impaired, this is referred to as color vision deficiency, for example red-green vision deficiency and green-blue vision deficiency. In the worst case, if you can no longer see one or more colors at all, this is called color blindness.
Men and color weakness
The following figures show just how many people are colorblind: Around eight percent of all men, but only around 0.4 percent of women suffer from it, reports the Professional Association of Ophthalmologists (BVA). Red-green deficiency is the most widespread, accounting for around 50 percent of all cases. This means that around 3.5 million people are affected in Germany alone. Total color blindness, in which those affected can only distinguish between light and dark, is much rarer - only one in 100,000 people suffer from it. They also have reduced visual acuity and suffer from severe glare [1].
The following images simulate how colorblind people see the world. You can see the original image and how it changes with red, green or blue blindness:

Figure 1: Simulation of different color blindnesses. Original (top left), red blindness (top right), green blindness (bottom left) and blue blindness (bottom right)
Possible problems when using a website
It becomes difficult for people with color vision deficiency when a certain meaning is associated with a color. Color blindness can blur the differences between different colors, making it more difficult to distinguish between them. This can be, for example, the colors of different data in a diagram. The problems that people encounter here are shown in Figure 2:
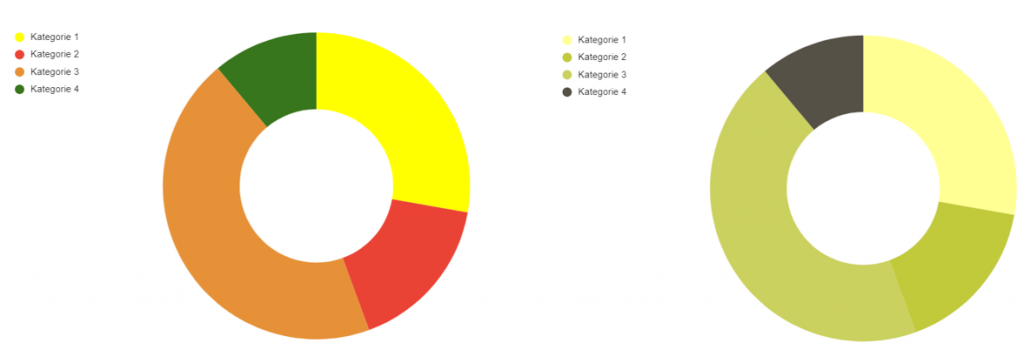
Figure 2: On the left the unchanged diagram, on the right with simulated green blindness
While all colors are easily distinguishable in the unaltered image on the left, the difference becomes much more difficult for a person with green blindness. The meaning of the color of buttons, the marking of areas on maps or general colored areas can also remain hidden from people with color blindness.
How Eye-Able adjusts the colors
To help people with color deficiency, Eye-Able has integrated the color deficiency function. As previously shown, there are different types and degrees of color blindness. This is why Eye-Able offers a total of six different modes. There is a specially adapted process for each color weakness, the option to remove the colors completely and to increase contrast or color saturation. The intensity can be adjusted for each of the functions. 100% means a correction for color blindness, while lower values compensate for color weakness. In order to make color differences more visible for those affected, the affected color areas are shifted towards visible colors. When correcting a red weakness, for example, the red colors are shifted towards the blue color spectrum. Eye-Able adjusts all visible colors on the website. The following illustration shows the benefits of this function:

Figure 3: Illustration of color correction using Ishihara test images (Source: Wellcome collection CC BY 4.0)
As can be seen in Figure 3, color differences can be better displayed for those affected by color correction. In addition to the respective color weakness modes, increasing the contrast or color saturation can also lead to an improvement. The following traffic light shows another example of how Eye-Able color correction can make color differences visible again:

Figure 4: Traffic light with normal colors (left), traffic light for people with red weakness (middle), traffic light for people with red weakness after Eye-Able correction (right)
Sources and further information
For those interested, here are some of our sources and further information material:
[2] https://www.sehtestbilder.de/sehtest/
You can also carry out an eye test yourself here. Caution: An online eye test can therefore only ever provide an indication. If you suspect a color vision deficiency, please consult an ophthalmologist.
[3] Françoise Viénot, Hans Brettel and John D. Mollon
Digital video colormaps for checking the legibility of displays by dichromats
Color Research and Application, 24(4): 243-252, 1999.